这次我们来继续介绍音量控制和进度条的实现
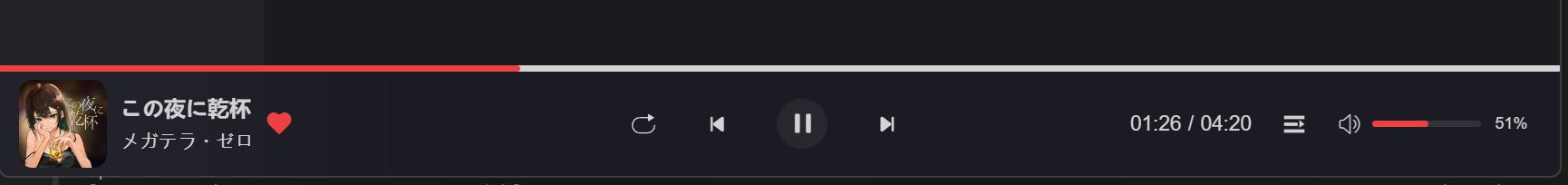
音量控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| // useUserStore
//当前播放器的音量
const volume = ref<number>(0.5)
// volume.vue
<template>
<div class="volume-box w-[150px] flex items-center">
<i v-if="volume !== 0" class="iconfont icon-yinliang" @click="volumeHandler(true)" />
<i v-else class="iconfont icon-jingyin" @click="volumeHandler(false)" />
<el-slider v-model="model" :show-tooltip="false" @input="input" @change="change"
style="width: 80px; overflow: hidden" />
<div class="volume-value text-[12px] ml-[10px]">
{{ model }}%
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, ref, watch } from 'vue'
import { useUserStore } from '@/store'
import { userAudio } from '@/components/MusicPlayer/index.vue'
interface Props {
audio?: userAudio
}
const props = defineProps<Props>()
const userStore = useUserStore()
/** slider 的百分比值 */
const model = ref(0)
/** 真实音量 0 ~ 1 */
const volume = computed(() => model.value / 100)
/** 初始化 / audio 就绪时同步音量 */
watch(
() => props.audio,
(audio) => {
if (!audio) return
const saved = userStore.volume
const initVolume = Number.isNaN(saved) ? 1 : saved
model.value = initVolume * 100
audio.volume = initVolume
},
{ immediate: true }
)
</script>
|
我们将音量先进行持久化存储,之后对父组件接收传来的audio实例进行监听并将值赋给它
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| /** 统一设置音量的方法(核心) */
const setVolume = (v: number) => {
if (!props.audio) return
props.audio.volume = v
userStore.volume = v
}
// 静音前的音量(0 ~ 1)
const beforeVolume = ref(1)
const volumeHandler = (mute: boolean) => {
if (mute && volume.value > 0) {
beforeVolume.value = volume.value
}
const target = mute
? 0
: beforeVolume.value || 1
model.value = target * 100
setVolume(target)
}
/** 拖动 slider */
const input = () => {
setVolume(volume.value)
}
/** 松手后同步到 store */
const change = () => {
userStore.volume = volume.value
}
|
setVolume的函数 接收到传来的将值赋给audio和存到store,静音的话我们这里处理一下,在点击静音前我们将之前一次的音量存起来,这样从静音到点到非静音时可以恢复
进度条功能实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| // ProgressBar.vue
<template>
<div class="base-progress-bar w-full" v-if="props.songs?.ar">
<el-slider
:class="{ 'is-dragging': isSeeking }"
v-model="slider"
:show-tooltip="false"
@input="onStart"
@change="onEnd"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { GetMusicDetailData } from '@/types/musicList'
import { useMusicStore } from '@/store'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
interface Props {
songs?: GetMusicDetailData
}
const props = defineProps<Props>()
const musicStore = useMusicStore()
/** 是否正在拖动 */
const isSeeking = ref(false)
/** 拖动时的临时时间 */
const tempTime = ref(0)
/** 歌曲总时长(秒) */
const duration = computed(() => {
return (musicStore.songs?.dt ?? 0) / 1000
})
/** slider 百分比 */
const slider = computed<number>({
get() {
const time = musicStore.currentTime
return duration.value
? (time / duration.value) * 100
: 0
},
set(val) {
const time = (val * duration.value) / 100
tempTime.value = time
}
})
const onStart = () => {
isSeeking.value = true
}
const onEnd = () => {
isSeeking.value = false
// 松手才真正设置 audio
window.$audio.time = tempTime.value
musicStore.currentTime = tempTime.value
}
</script>
|
这里的处理可以看一下在拖动的时候这里并没有直接给audio.current直接赋值而是在end的时候再进行赋值处理
window.$audio.time = tempTime.value这里的可以回顾一下我们第一章介绍的
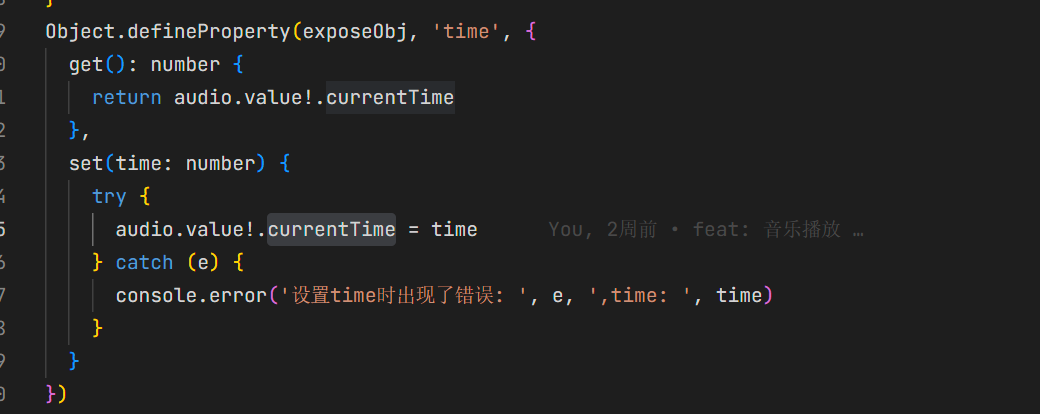
audio.currentTime是双精度浮点型,所以musicStore里面的currentTime和我们设置的都必须是以秒为单位的,这里就可以理解我这里获取duration和在set里面Time的处理了

